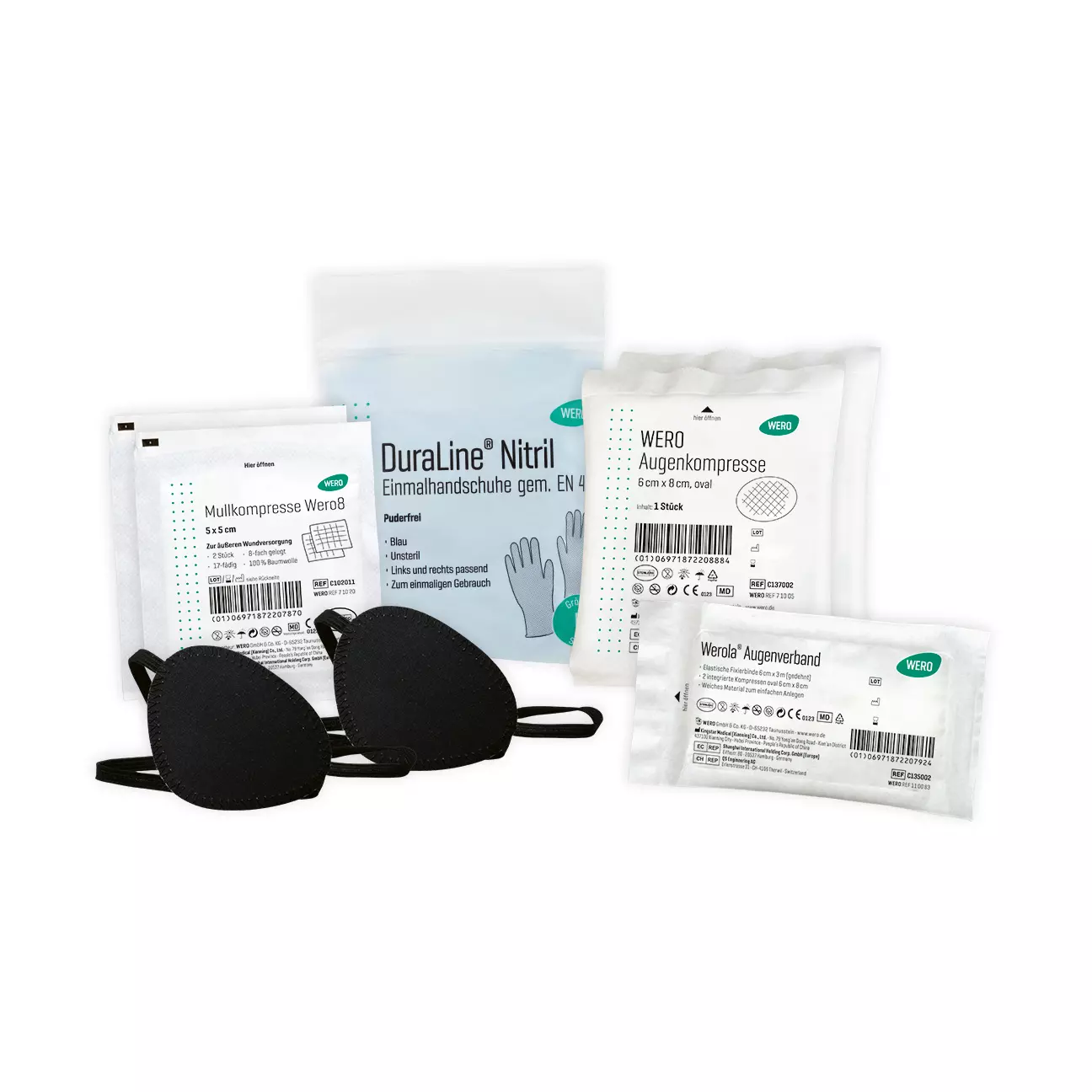
Treating chemical burns correctly
Eye rinses, compresses & more
Available, delivery time: 1-3 days
Content: 2 piece (€1.67* / 1 piece)
Available, delivery time: 1-3 days
Available, delivery time: 1-3 days
Available, delivery time: 1-3 days
What is the difference between a burn and a chemical burn?
In the case of a chemical burn, tissue destruction can only be stopped by completely removing the substance, whereas in the case of burns there is often only brief contact.
What does an eye burn mean?
The eye is usually protected from foreign bodies and dehydration by the eyelid closure reflex. If contact with the inside of the eye nevertheless occurs as a result of an accident or an attack with corrosive chemicals, severe redness, spasmodic twitching, swelling and excessive tearing can occur. Even a small splash can cause irreversible damage to the affected eye: Cells can die, circulatory disorders or corneal clouding can occur, which can reduce visual acuity. Rapid, targeted initial treatment is very important here.
Which substances and chemicals cause chemical burns to the eyes?
- Chemical burns caused by organic solvents or liquid household cleaning agents such as descaling agents
- Acid burns (hydrochloric acid, fruit acid, bleach or car batteries)
- Chemical burns from alkalis
What are the most common causes of eye burns?
Eye burns are usually caused by plaster or cement, chemical cleaning agents and cleaning products. These are alkalis, which are particularly dangerous as they can penetrate even deeper into the tissue than acids.
How are eye burns treated?
The eye should be cleaned immediately with an eye wash or eye shower. The designation "P" identifies WERO eye rinses that are effective against chemicals. Cover the healthy eye. An ophthalmologist should be consulted immediately afterwards. The eye is then rinsed further and eye drops are administered if necessary. Corneal transplantation may be necessary for particularly severe injuries.
How are chemical burns on the body treated?
- Dial emergency number
- Pay attention to your own safety (wear protective gloves)
- In the event of chemical burns, carefully remove all wet clothing, including shoes and socks, immediately.
- Immediately rinse the affected area under running water.
- If no water is available, use cellulose gauze compresses and dab corrosive substances with them.
- Each swab may only be used once.
- Apply a dressing.
How can I protect myself from a chemical burn?
- Handle chemical substances with care: Find out about the correct application, warnings and protective measures before use.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): This includes safety goggles, gloves, face masks and gowns.
- Labelling of chemical substances: Store cleaning agents in their original containers and record them in a hazardous substances register.
- Safe storage: Keep chemical substances out of the reach of children and animals.